Introduction:
Have you heard of smart contracts but aren't quite sure what they are or how they work? You're not alone! In this blog, I will provide a simple introduction to smart contracts and explain how they work.

What Are Smart Contracts?
Imagine that you and your friend want to make a deal. You agree that you will give your friend a toy in exchange for some candy.
A smart contract is like a special kind of rule or agreement that makes sure the deal is fair and that both you and your friend follow through with what you said you would do.
The rules are written in a special computer language, and they are stored on a big computer network that a lot of people can see and use. This way, everyone knows that the rules are fair and that nobody can change them without everyone else knowing.
Once the rules are set, the computer network will automatically make sure that both you and your friend follow them. If you give your friend the toy, the network will make sure your friend gives you the candy. And if either of you doesn't follow the rules, the network will not let the deal go through.
So a smart contract is like a special kind of rule that uses computers to make sure that deals are fair and that everyone follows through with what they said they would do.
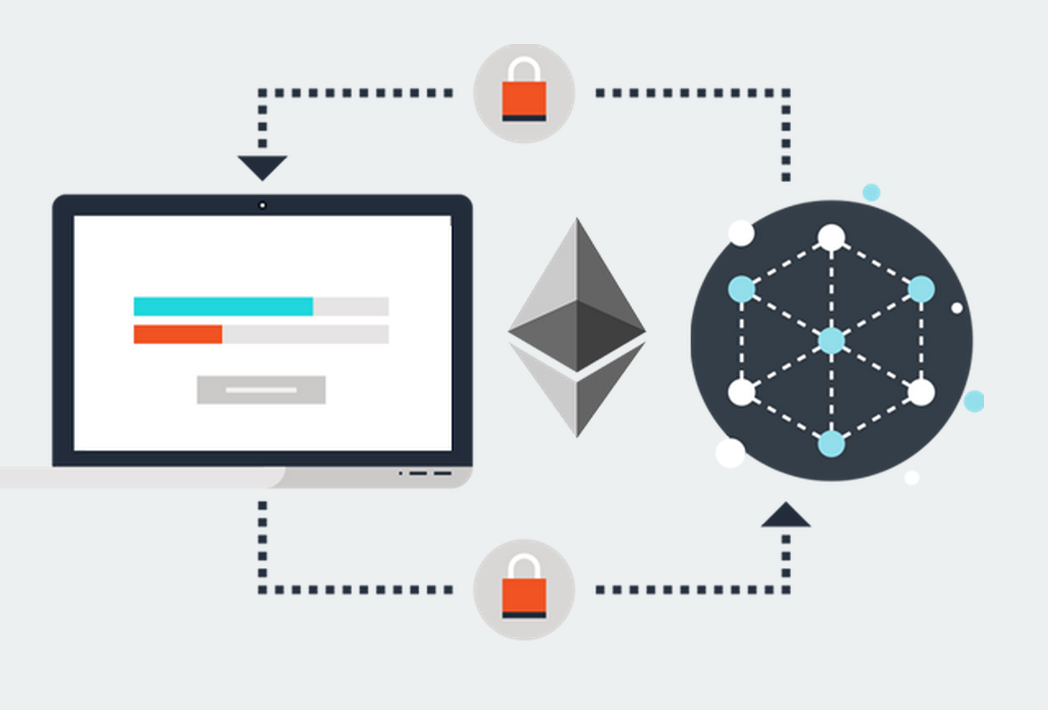
At their core, smart contracts are simply computer programs that can automatically execute the terms of an agreement when certain conditions are met. They are designed to facilitate, verify, and enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract.
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. The code and the agreements contained therein exist across a distributed, decentralized blockchain network.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts are executed on the blockchain, which is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions and agreements. The blockchain is secured through cryptography, which ensures that the data on the blockchain is tamper-proof and cannot be altered.
Solidity is a programming language that is used to write smart contracts for the Ethereum blockchain. It allows developers to create and implement complex smart contracts on the Ethereum platform.
The most commonly used language for writing smart contracts is Solidity, which was specifically designed for the Ethereum platform. Other popular languages for writing smart contracts include Vyper, Bamboo, and C++.
When a smart contract is created, it is stored on the blockchain and can be accessed by any party on the network. The terms of the contract are written in code, and the contract is triggered when certain conditions are met. For example, a smart contract could be set up to automatically release payment to a seller when a buyer receives a product.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
There are several benefits to using smart contracts, including:
Automation: Smart contracts can automate complex processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing the speed and efficiency of executing agreements.
Transparency: The terms of a smart contract are recorded on the blockchain and can be verified by any party on the network. This increases transparency and trust.
Security: The blockchain is secured through cryptography, which makes it tamper-proof and ensures the integrity of the data.
Cost savings: Smart contracts can reduce the need for intermediaries, which can result in cost savings for businesses.
Use Cases for Smart Contracts
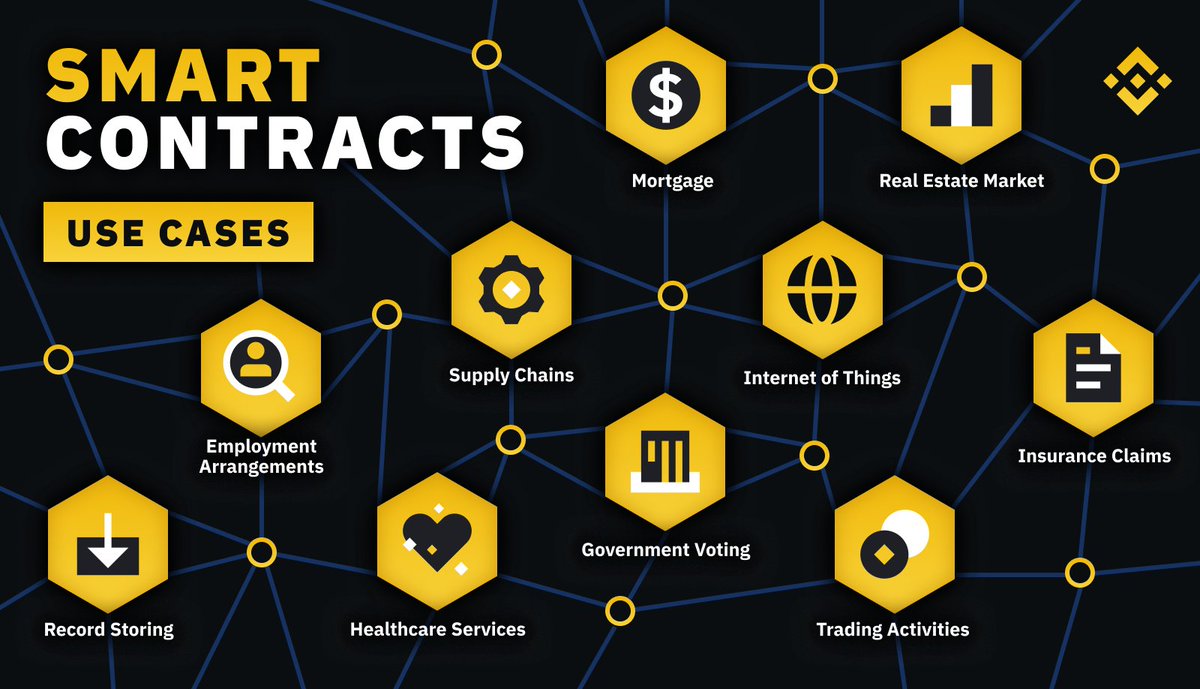
There are many potential use cases for smart contracts, including:
Supply chain management
Smart contracts can be used to automate and streamline the process of tracking and managing the movement of goods through the supply chain. They can be used to verify the authenticity of products, track the movement of goods, and release payments to suppliers.
Voting
Smart contracts can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems that are less susceptible to fraud and manipulation. By storing the voting data on the blockchain, smart contracts can help to ensure the integrity of the voting process.
Music rights management
Smart contracts can be used to automatically distribute royalties to artists and other rights holders when their music is played or downloaded. This can help to ensure that artists are fairly compensated for their work.
Real estate
Smart contracts can be used to automate the process of buying and selling real estate. They can be used to verify the ownership of a property, facilitate the transfer of ownership, and release payment to the seller.
Insurance
Smart contracts can be used to automate the claims process in the insurance industry. They can be used to verify the occurrence of an event (such as a car accident), calculate the payout, and automatically release payment to the policyholder.
Challenges associated with Smart Contracts
Despite their potential benefits, smart contracts are not without their challenges.
One of the biggest challenges is the need for widespread adoption and standardization. For smart contracts to reach their full potential, they need to be adopted by a critical mass of users and businesses. Additionally, there needs to be some level of standardization to ensure compatibility between different smart contract platforms.
Another challenge is the need for strong technical expertise. Because smart contracts are written in code, they require a certain level of technical knowledge to be created and deployed. This can be a barrier for some businesses and individuals who may not have the necessary expertise.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are computer programs that can automatically execute the terms of an agreement when certain conditions are met. They have the potential to revolutionize the way we do business by automating complex processes, reducing the need for intermediaries, and increasing transparency and trust. While still in their early stages, the adoption of smart contracts is growing, and we can expect to see more and more use cases in the future.
If you enjoyed reading this blog and this helped you understand the basics of smart contracts, please consider following me on Twitter (@uday03meh) and follow me on Hashnode(@uday03meh) for Smart Contracts: Part 2